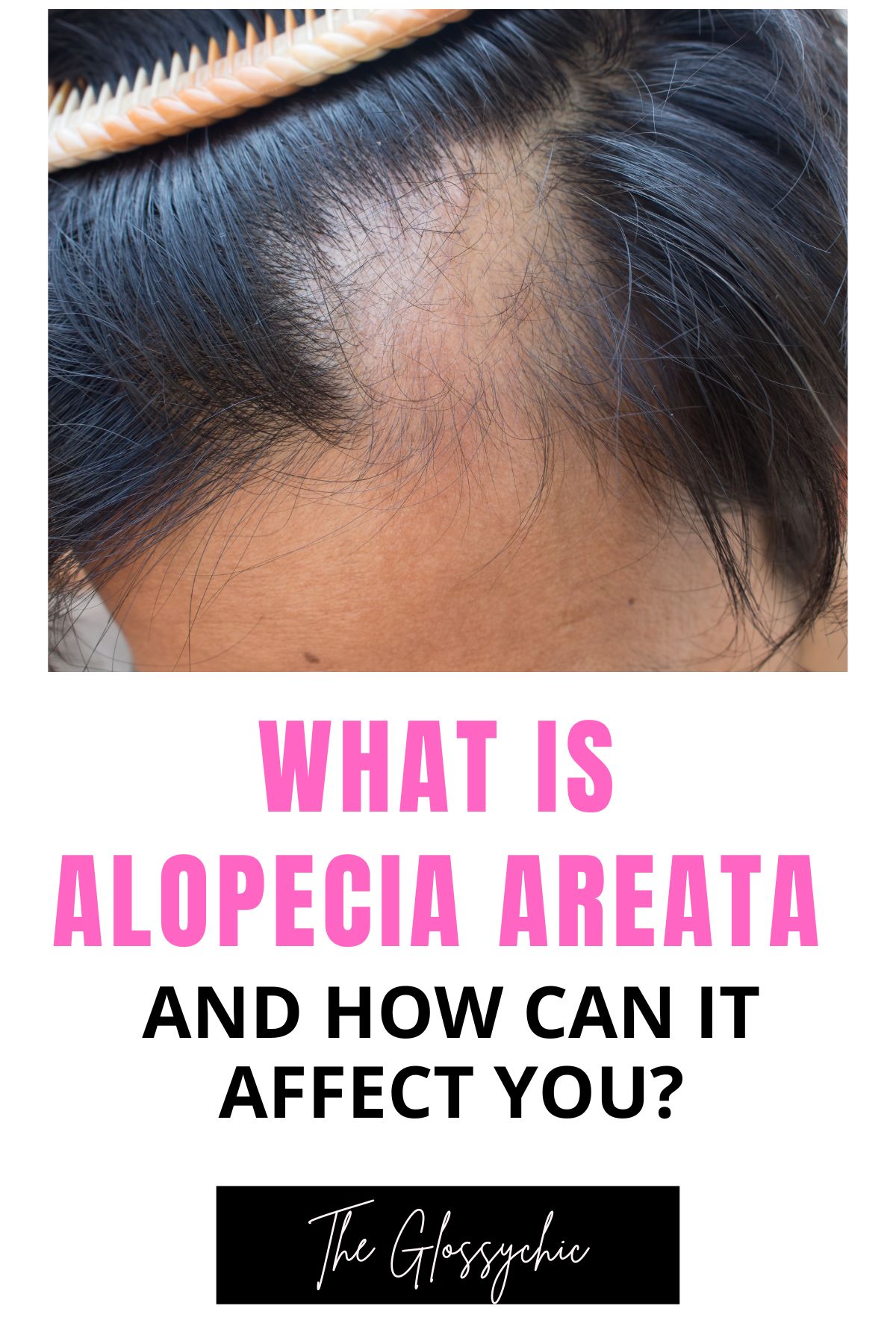
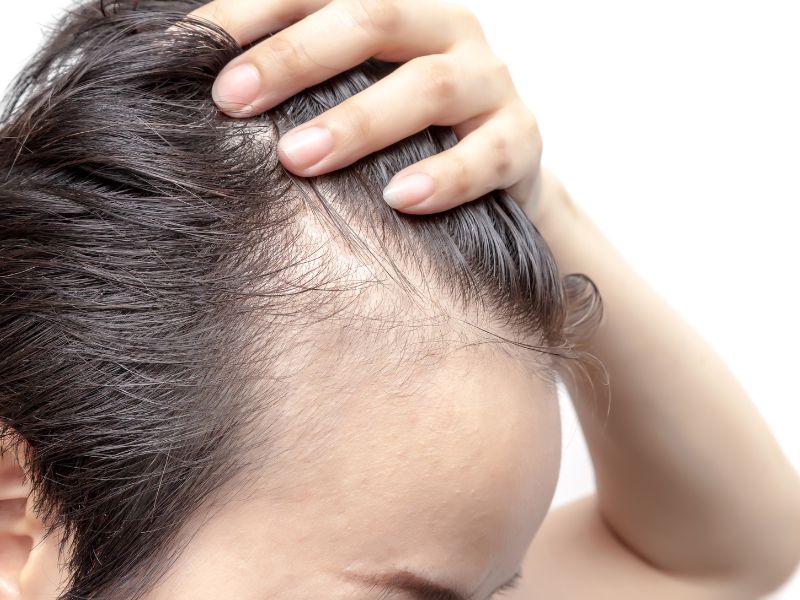
When most people think of hair loss, they think of aging or genetics. And while those can certainly be factors, other causes of hair loss are less well-known. One of those is alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder that can cause patchy hair loss on the scalp, face, and elsewhere on the body.
Alopecia areata is more common than you might think, affecting as many as 6.8 million people in the United States alone. Here’s what you need to know about this condition.

What is Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss on the face, scalp, and elsewhere on the body. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be triggered by stress or other factors. The condition affects both men and women and can occur at any age. There are three types of alopecia areata:
The 3 types of alopecia areata
Alopecia totalis
Unlike some forms of hair loss, alopecia totalis is not just temporary or caused by styling damage. It’s an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body’s immune system attacks the hair follicles and prevents them from producing new hair.
It usually begins with small patches of baldness that gradually spread until all scalp hair is lost. Unfortunately, there isn’t a known cure for alopecia totalis. However, treatments such as corticosteroid injections or topical solutions can help slow down hair loss and even encourage regrowth in some cases.
Alopecia universalis
Alopecia universalis is a type of hair loss that results in the complete loss of all body hair, including eyebrows and eyelashes. It’s somewhat rare, affecting about 1 in every 50,000 people. While it can occur at any age, it often develops during childhood or adolescence.
The cause of alopecia universalis is not entirely understood, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder in which the body mistakenly attacks its own hair follicles.
Treatment options include corticosteroid injections, topical immunotherapy, and UV light therapy. Unfortunately, there is currently no known cure for alopecia universalis. However, some people have reported success with natural remedies such as aromatherapy and acupuncture.
Ophiasis
Ophiasis is a type of hair loss that typically presents as a thinning, or “balding,” in a specific pattern along the person’s hairline. This pattern typically resembles the shape of a wave or an “S” shape. It can also cause little “islands” of hair to remain, giving it the nickname “island ophiasis.”
This hair loss is most common in men. Usually, it occurs in the later stages of androgenetic alopecia (typically male/female pattern baldness). Treatment options for ophiasis include medications like minoxidil and topical corticosteroids. Hair transplant can also be successful in restoring areas affected by ophiasis.
How Alopecia May Affect You
Alopecia areata is a relatively common autoimmune disorder that can have a significant impact on mental health, but many ways can help you manage your condition.
Many people with alopecia areata can lead normal, healthy lives. However, the condition can have a significant impact on mental health. The anxiety and insecurity caused by hair loss can lead to depression, social isolation, and other mental health issues.
If you’re struggling to cope with hair loss, it’s vital to seek professional help. There are support services for mental health that can help you manage your condition and live a full, satisfying life.
Alopecia Areata Treatment Options
Alopecia areata has no cure, but some treatments may help promote hair growth or camouflage baldness. The following are some treatment alternatives for alopecia areata:
- Steroid injections: Steroids can help reduce inflammation and promote hair growth. They are usually injected into the affected areas every four to eight weeks.
- Oral medications: Oral medications such as Rogaine (minoxidil) can help promote hair growth in some people with mild alopecia areata. Side effects may include itchiness, dryness, or scalp irritation.
- Topical medications include corticosteroid creams or ointments that can be applied to the scalp to help reduce inflammation and promote hair growth. Side effects may include skin thinning or lightening in the areas where the medication was applied.
- Light therapy: Light therapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light regularly over a period of time. It can help stimulate hair growth in some people with alopecia areata but may not be effective for everyone. Possible side effects include skin damage such as sunburn or skin cancer.
- Hairpieces or camouflage: Hairpieces (such as wigs) can help cover up patches of baldness caused by alopecia areata until your own hair grows back. There are also products available (such as Toppik) that can be used to disguise areas of thinning hair by adding color and texture without affecting your own hair underneath.
Final thoughts
Hair loss can be a difficult thing to deal with, but it’s important to remember that you’re not alone. Many people are dealing with hair loss, and there are treatments available that can help. Don’t let this condition take over your life-seek professional help if you struggle to cope. With the right support, you can live a happy and fulfilling life.